Lecture 11b Dealing with spurious minima in Hopfield Nets (Hopfield Nets의 가짜 미니 마 다루기)
The storage capacity of a Hopfield net
- • Using Hopfield’s storage rule the capacity of a totally connected net with N units is only about 0.15N memories.
- – At N bits per memory this is only 0.15*N^2 bits.
- – This does not make efficient use of the bits required to store the weights.
- • The net has N^2 weights and biases.
- • After storing M memories, each connection weight has an integer value in the range [–M, M].
- • So the number of bits required to store the weights and biases is: N^2 log(2M +1)
• Hopfield의 스토리지 규칙을 사용하면 N 단위로 완전히 연결된 넷의 용량은 약 0.15N 메모리에 불과합니다.
메모리 당 N 비트에서 이것은 0.15*N^2 비트 일뿐입니다.
이것은 가중치 저장에 필요한 비트를 효율적으로 사용하지 않습니다.
• 그물에는 무게와 biases이 있습니다.
• M 개의 메모리를 저장 한 후 각 연결 가중치는 [-M, M] 범위의 정수 값을 가집니다.
• 따라서 가중치 및 바이어스를 저장하는 데 필요한 비트 수는 다음과 같습니다. N^2 log (2M +1)
Spurious minima limit capacity
Each time we memorize a configuration, we hope to create a new energy minimum.
– But what if two nearby minima merge to create a minimum at an intermediate location?
– This limits the capacity of a Hopfield net.
우리가 설정을 암기 할 때마다 우리는 새로운 에너지 최소를 만들기를 바랍니다.
그러나 중간에 두 개의 미니 마가 병합되어 중간 위치에 최소값을 만들면 어떻게 될까요?
이것은 Hopfield net의 용량을 제한합니다.
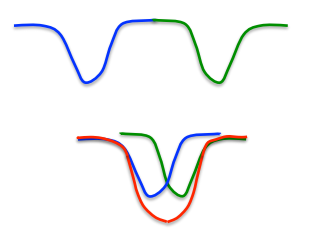
The state space is the corners of a hypercube. Showing it as a 1-D continuous space is a misrepresentation.
상태 공간은 하이퍼 큐브의 모서리입니다. 이를 1 차원 연속 공간으로 표시하는 것은 허위 진술입니다.
Avoiding spurious minima by unlearning
- • Hopfield, Feinstein and Palmer suggested the following strategy:
- – Let the net settle from a random initial state and then do unlearning.
- – This will get rid of deep, spurious minima and increase memory capacity.
- • They showed that this worked.
- – But they had no analysis.
- • Crick and Mitchison proposed unlearning as a model of what dreams are for.
- – That’s why you don’t remember them (unless you wake up during the dream)
- • But how much unlearning should we do?
- – Can we derive unlearning as the right way to minimize some cost function?
• Hopfield, Feinstein 및 Palmer는 다음과 같은 전략을 제안했습니다.
그물을 무작위로 초기 상태에서 정한 다음 unlearning 합니다.
이렇게하면 깊고 가짜 인 미니 마를 없애고 메모리 용량을 늘릴 수 있습니다.
• 그들은 이것이 효과가 있음을 보여주었습니다.
-하지만 분석은 없었어요.
• 크릭 (Crick)과 미치슨 (Mitchison)은 꿈이 무엇을위한 모델인지에 대한 unlearning을 제안했습니다.
- 그래서 기억하지 못하는 것입니다 (꿈에서 깨어나지 않는 한)
• 그러나 우리는 얼마나 많은 일을해야 하는가?
- 일부 비용 기능을 최소화하는 올바른 방법으로 비 상식을 도출 할 수 있습니까?
Increasing the capacity of a Hopfield net
- • Physicists love the idea that the math they already know might explain how the brain works.
- – Many papers were published in physics journals about Hopfield nets and their storage capacity.
- • Eventually, Elizabeth Gardiner figured out that there was a much better storage rule that uses the full capacity of the weights.
- • Instead of trying to store vectors in one shot, cycle through the training set many times.
- – Use the perceptron convergence procedure to train each unit to have the correct state given the states of all the other units in that vector.
- • Statisticians call this technique “pseudo-likelihood”.
• 물리학 자들은 이미 알고있는 수학이 뇌가 어떻게 작용하는지 설명 할 수 있다는 생각을 좋아합니다.
- Hopfield net과 저장 용량에 관한 물리학 저널에 많은 논문이 실렸습니다.
• 결국 Elizabeth Gardiner는 가중치의 전체 용량을 사용하는 스토리지 규칙이 훨씬 우수하다는 것을 알아 냈습니다.
• 벡터를 한 번에 저장하는 대신 여러 번 훈련 세트를 반복하십시오.
- 퍼셉트론 수렴 절차를 사용하여 각 단위가 해당 벡터의 다른 모든 단위의 상태를 고려하여 올바른 상태로 훈련하도록합니다.
• 통계학자는이 기술을 "의사 가능성 (pseudo-likelihood)"이라고 부릅니다.